Selection bias
What If: Chapter 8
Elena Dudukina
2021-02-18
1 / 16
Selection bias
Classic definition
- The magnitude of the association is different for participants and non-participants
Structural definition
- Occurs when conditioning on the common child or its descendants of two variables
Encompasses various biases
2 / 16
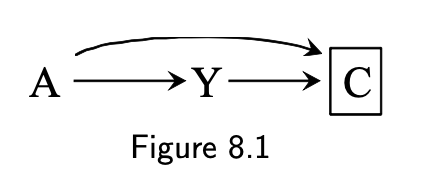
8.1 The structure of selection bias
DAG:
- A: exposure (folic acid supplements)
- Y: outcome, binary (cardiac malformation)
- C: common effect (death before birth) observed only among live-born children (C=0)
3 / 16
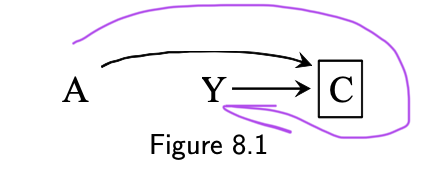
Under the null
The biasing path A ➡️ [C] ⬅️ Y
The associational risk ratio does not equal causal risk ratio
- Pr[Y=1|A=1,C=0]Pr[Y=1|A=0,C=0] is not Pr[Ya=1]Pr[Ya=0]
4 / 16
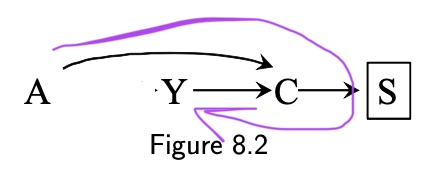
Selection bias
DAG:
- A: exposure (folic acid supplements)
- Y: outcome, binary (cardiac malformation)
- C: common effect (death before birth) observed only among live-born children (C=0)
- S: parental grief (restricted to S=0)
Under null we would still see an association between A and Y due to the collider stratification bias
- The biasing path A ➡️ [C] ⬅️ Y
5 / 16
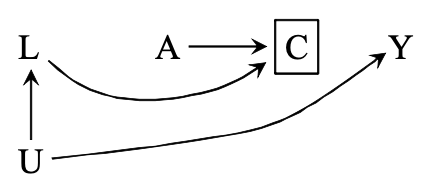
Selection bias
- DAG 8.3:
- A: anti-retroviral treatment
- Y: 3-year risk of death
- U: unmeasured, immunosuppression (U=1 are under greater risk of death)
- C: censored (C=1)
- L: unmeasured, immunosuppression symptoms
Biasing path:
- A ➡️ [C] ⬅️ L ⬅️ U ➡️ Y
6 / 16
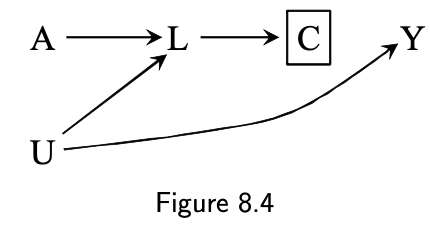
Selection bias
- DAG 8.4:
- A: anti-retroviral treatment
- Y: 3-year risk of death
- U: unmeasured, immunosuppression (U=1 are under greater risk of death)
- C: censored (C=1)
- L: unmeasured, immunosuppression symptoms
Biasing path:
- A ➡️ [L] ⬅️ U ➡️ Y
7 / 16
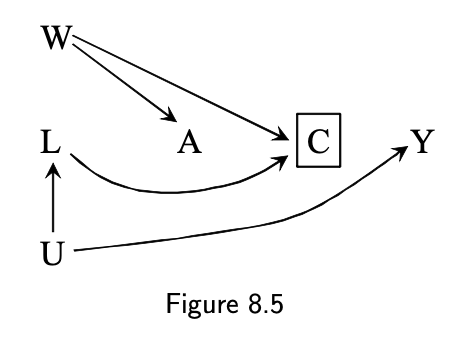
Selection bias
- DAG 8.5 (M-bias):
- A: anti-retroviral treatment
- Y: 3-year risk of death
- U: unmeasured, immunosuppression (U=1 are under greater risk of death)
- C: censored (C=1)
- L: unmeasured, immunosuppression symptoms
- W: unmeasured, lifestyle
8 / 16
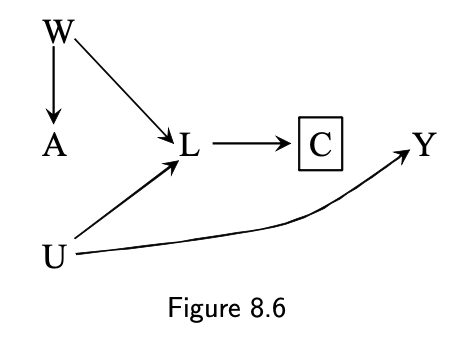
Selection bias
- DAG 8.6 (M-bias):
- A: anti-retroviral treatment
- Y: 3-year risk of death
- U: unmeasured, immunosuppression (U=1 are under greater risk of death)
- C: censored (C=1)
- L: unmeasured, immunosuppression symptoms
- W: unmeasured, lifestyle
9 / 16
8.2 Examples of selection bias
- Differential loss to follow-up/informative censoring (8.3-8.6)
- Missing data bias, non-response bias
- Missing data on the outcome for any reason (8.3-8.6)
- Healthy worker bias
- U: unmeasured, underlying health
- C: at work or not (C=0 being at work)
- Self-selection bias, volunteer bias
- Selection affected by treatment received before study entry
Selection bias can occur in any follow-up study (observational or RCT)
- Those who stayed in the study (uncensored, C=0) are not exchangeable with those who did not stay in the study (censored, C=1)
- Can only compute observational Pr[Y=1|A=1,C=0]Pr[Y=1|A=0,C=0], but not counterfactual Pr[YA=1,C=c]Pr[YA=0,C=c] under both levels of C={0, 1}
10 / 16
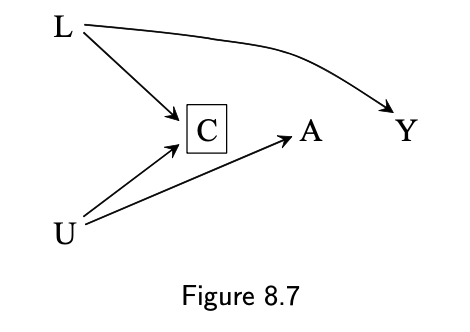
8.3 Selection bias and confounding
Sources of lack of exchangeability:
- Confounding
- Selection bias
DAG 8.7:
- A: physical activity
- Y: heart disease
- L: family SES
- C: becoming a firefighter (restricted to C=1)
- U: unmeasured, personal preference for physical activity professions
There is no confounding between A and Y Pr[Y=1|A=1,C=0]Pr[Y=1|A=0,C=0] is Pr[Ya=1]Pr[Ya=0]
11 / 16
8.4 Selection bias and censoring
- Censoring as "treatment"
- Identifiability conditions of exchangeability, positivity, and consistency hold for both A and C
- Analytical methods
12 / 16
8.5 How to adjust for selection bias
- IP weighting (or standardization)
- Assigning a weight to each selected individual (C = 0) that accounts for the individuals with same A and L, but C=1
- Weights constructed from the probability of selection model: Pr[C=0|L,A]
- Effect measure in the population had no one been censored
13 / 16
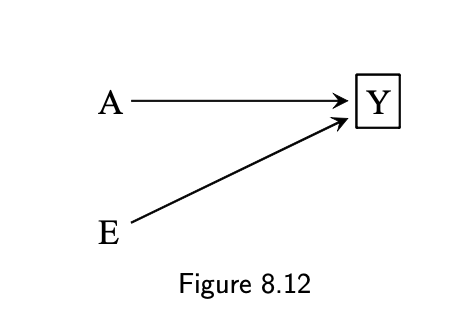
8.6 Selection without bias
- A: surgery
- Y: death
- E: haplotype
14 / 16
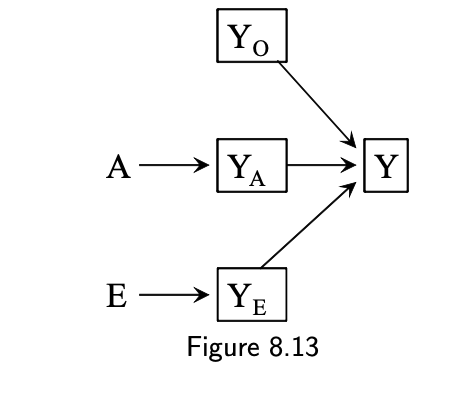
- "Collider stratification is not always a source of selection bias"
15 / 16
References
Hernán MA, Robins JM (2020). Causal Inference: What If. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC (v. 31jan21)
16 / 16